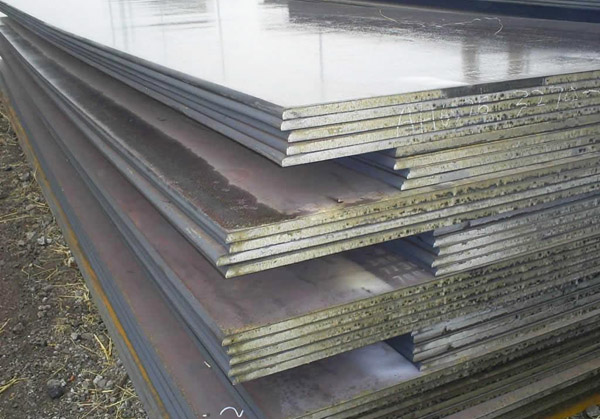
Stainless Steel Plate

Properties of Stainless Steel Sheets:
- Oxidation:
High oxidation resistance in air at ambient temperature is normally achieved with additions of a minimum of 13% chromium, and up to 26% is used for harsh environments.
- Acids
Stainless steel is generally highly resistant to attack from acids, but this quality depends on the kind and concentration of the acid, the surrounding temperature, and the type of steel.
- Bases
The 300 series of stainless steel grades is unaffected by any of the weak bases such as ammonium hydroxide, even in high concentrations and at high temperatures.
- Electricity and magnetism
Similarly to steel, stainless steel is a relatively poor conductor of electricity, with a lower electrical conductivity than that of copper.
Chemical Compositions of Martensite, Ferrite, Austenite and Diphasic Stainless Steel plates:
| Grade | Mark | Chemical Compositions(%) | ||||||||||
| C | Cr | Ni | Mn | P | S | Mo | Si | Cu | N | Others | ||
| 201 | 1Cr17Mn 6Ni5N | ≤0.15 | 16.00- 18.00 | 3.50- 5.50 | 5.50- 7.50 | ≤0.060 | ≤0.03 | - | ≤1.00 | - | ≤0.25 | - |
| 201L | 03Cr17Mn 6Ni5N | ≤0.03 | 16.00- 18.00 | 3.50- 5.50 | 5.50- 7.50 | ≤0.060 | ≤0.03 | ≤1.00 | ≤0.25 | |||
| 202 | 1Cr18Mn 8Ni5N | ≤0.15 | 17.00- 19.00 | 4.00- 6.00 | 7.50- 10.00 | ≤0.060 | ≤0.03 | ≤1.00 | - | ≤0.25 | - | |
| 204 | 03Cr16Mn 8Ni2N | ≤0.03 | 15.00- 17.00 | 1.50- 3.50 | 7.00- 9.00 | 0.15- 0.30 | ||||||
| China | 1Cr18Mn10Ni 5Mo3N | ≤0.10 | 17.00- 19.00 | 4.00- 6.00 | 8.50- 12.00 | 2.8- 3.5 | 0.20- 0.30 | |||||
| Russia | 2Cr13Mn 9Ni4 | 0.15- 0.25 | 12.00- 14.00 | 3.70- 5.00 | 8.00- 10.00 | |||||||
| China | 2Cr15Mn 15Ni2N | 0.15- 0.25 | 14.00- 16.00 | 1.50- 3.00 | 14.00- 16.00 | 0.15- 0.30 | ||||||
| 1Cr18Mn 10Ni5Mo3N | ≤0.15 | 17.00- 19.00 | 4.00- 6.00 | 8.50- 12.00 | ≤0.060 | ≤0.03 | 2.8- 3.5 | ≤1.00 | - | 0.20- 0.30 | - | |
| 301 | 1Cr17Ni7 | ≤0.15 | 16.00- 18.00 | 6.00- 8.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.065 | ≤0.03 | - | ≤1.00 | - | - | - |
| 302 | 1Cr18Ni9 | ≤0.15 | 17.00- 19.00 | 8.00- 10.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.03 | - | ≤1.00 | - | - | - |
| 303 | Y1Cr18Ni9 | ≤0.15 | 17.00- 19.00 | 8.00- 10.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.20 | ≤0.03 | 1) | ≤1.00 | - | - | - |
| 303se | Y1Cr18Ni 9Se | ≤0.15 | 17.00- 19.00 | 8.00- 10.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.20 | ≤0.03 | - | ≤1.00 | - | - | Se≥0.15 |
| 304 | 0Cr18Ni9 | ≤0.07 | 17.00- 19.00 | 8.00- 10.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.03 | - | ≤1.00 | - | - | - |
| 304L | 00Cr19Ni10 | ≤0.03 | 18.00- 20.00 | 8.00- 10.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.03 | - | ≤1.00 | - | - | - |
| 304N1 | 0Cr19Ni9N | ≤0.08 | 18.00- 20.00 | 7.00- 10.50 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.03 | - | ≤1.00 | - | 0.10- 0.25 | - |
| 304N2 | 0Cr18Ni 10NbN | ≤0.08 | 18.00- 20.00 | 7.00- 10.50 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.03 | - | ≤1.00 | - | 0.15- 0.30 | Nb≤0.15 |
| 304LN | 00Cr18Ni 10N | ≤0.03 | 17.00- 19.00 | 8.50- 11.50 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.03 | - | ≤1.00 | - | 0.12- 0.22 | - |
| 305 | 1Cr18Ni12 | ≤0.12 | 17.00- 19.00 | 10.50- 13.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.03 | - | ≤1.00 | - | - | |
| 309S | 0Cr23Ni13 | ≤0.08 | 22.00- 24.00 | 12.00- 15.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.03 | - | ≤1.00 | - | - | |
| 310S | 0Cr25Ni20 | ≤0.08 | 24.00- 26.00 | 19.00- 22.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.03 | - | ≤1.00 | - | - | - |
| 316 | 0Cr17Ni 12Mo2 | ≤0.08 | 16.00- 18.50 | 10.00- 14.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.03 | 2.00- 3.00 | ≤1.00 | - | - | - |
| 1Cr18Ni 12Mo2Ti6) | ≤0.12 | 16.00- 19.00 | 10.00- 14.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.03 | 1.80- 2.50 | ≤1.00 | - | - | Ti5 (C%-0.02)~ 0.08 | |
| 0Cr18Ni 12Mo2Ti | ≤0.08 | 16.00- 19.00 | 10.00- 14.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.03 | 1.80- 2.50 | ≤1.00 | - | - | Ti5*C%- 0.70 | |
| 316L | 00Cr17Ni 14Mo2 | ≤0.03 | 16.00- 18.00 | 12.00- 15.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.03 | 2.00- 3.00 | ≤1.00 | - | - | - |
| 316N | 0Cr17Ni 12Mo2N | ≤0.08 | 16.00- 18.00 | 10.00- 14.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.03 | 2.00- 3.00 | ≤1.00 | - | - | - |
| 316N | 00Cr17Ni 13Mo2N | ≤0.03 | 16.00- 18.50 | 10.50- 14.50 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.03 | 2.00- 3.00 | ≤1.00 | - | - | - |
| 316J1 | 0Cr18Ni 12Mo2Cu2 | ≤0.08 | 17.00- 19.00 | 10.50- 14.50 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.03 | 1.20- 2.75 | ≤1.00 | 1.00- 2.50 | - | - |
| 316J1L | 00Cr18Ni 14Mo2Cu2 | ≤0.03 | 17.00- 19.00 | 12.00- 16.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.03 | 1.20- 2.75 | ≤1.00 | 1.00- 2.50 | - | - |
| 317 | 0Cr19Ni 13Mo3 | ≤0.12 | 18.00- 20.00 | 11.00- 15.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.03 | 3.00- 4.00 | ≤1.00 | - | - | - |
| 317L | 00Cr19Ni 13Mo3 | ≤0.08 | 18.00- 20.00 | 11.00- 15.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.03 | 3.00- 4.00 | ≤1.00 | - | - | - |
| 1Cr18Ni 12Mo3Ti6) | ≤0.12 | 16.00- 19.00 | 11.00- 14.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.03 | 2.50- 3.50 | ≤1.00 | - | - | Ti5 (C%-0.02)~ 0.08 | |
| 0Cr18Ni 12Mo3Ti | ≤0.08 | 16.00- 19.00 | 11.00- 14.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.03 | 2.50- 3.50 | ≤1.00 | - | - | Ti5*C%- 0.70 | |
| 317J1 | 0Cr18Ni 16Mo5 | ≤0.04 | 16.00- 19.00 | 15.00- 17.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.03 | 4.00- 6.00 | ≤1.00 | - | - | - |
| 321 | 1Cr18Ni9Ti6) | ≤0.12 | 17.00- 19.00 | 8.00- 11.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.030 | - | ≤1.00 | - | - | Ti5 (C%-0.02)~ 0.08 |
| 0Cr18Ni10Ti | ≤0.08 | 17.00- 19.00 | 9.00- 12.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.03 | - | ≤1.00 | - | - | Ti≥5*C% | |
| 347 | 0Cr18Ni11Nb | ≤0.08 | 17.00- 19.00 | 9.00- 13.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.03 | - | ≤1.00 | - | - | Nb≥10*C% |
| XM7 | 0Cr18Ni9Cu3 | ≤0.08 | 17.00- 19.00 | 8.50- 10.50 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.03 | - | ≤1.00 | 3.00- 4.00 | - | - |
| XM15J1 | 0Cr18Ni13Si4 | ≤0.08 | 15.00- 20.00 | 11.50- 15.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.03 | - | 3.00- 5.00 | - | (2) | |
Stainless steel, also known as inox steel, is a steel alloy with a minimum of 10.5% chromium content by mass.
Stainless steel does not readily corrode, rust or stain with water as ordinary steel does. However, it is not fully stain-proof in low-oxygen, high-salinity, or poor air-circulation environments.There are different grades and surface finishes of stainless steel to suit the environment the alloy must endure. Stainless steel is used where both the properties of steel and corrosion resistance are required.
Stainless steel differs from carbon steel by the amount of chromium present. Unprotected carbon steel rusts readily when exposed to air and moisture. This iron oxide film (the rust) is active and accelerates corrosion by forming more iron oxide; and, because of the greater volume of the iron oxide, this tends to flake and fall away. Stainless steels contain sufficient chromium to form a passive film of chromium oxide, which prevents further surface corrosion by blocking oxygen diffusion to the steel surface and blocks corrosion from spreading into the metal's internal structure, and, due to the similar size of the steel and oxide ions, they bond very strongly and remain attached to the surface.